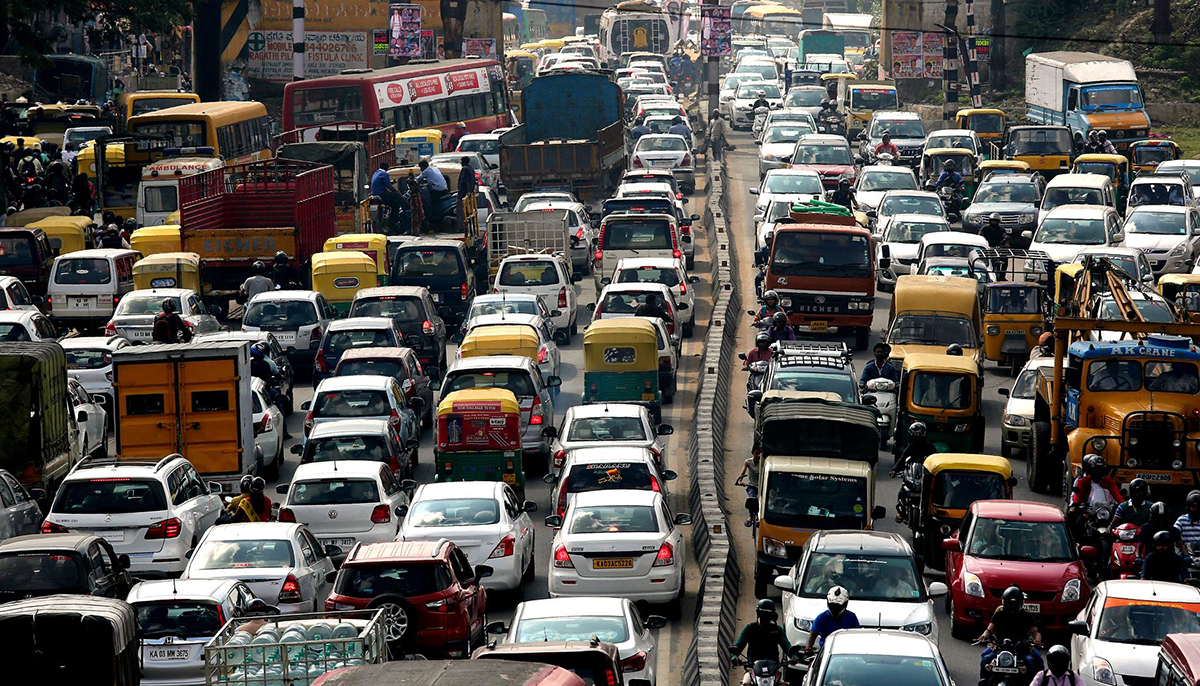
India will adopt the Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedure (WLTP) for BS6 emission testing starting April 1, 2027, marking a major shift in how vehicle emissions and fuel efficiency are measured.
The new WLTP framework will apply to M1 and M2 category vehicles, including passenger cars, SUVs, MPVs, and commercial passenger vans and buses with a gross vehicle weight below five tonnes. Testing will take place on chassis dynamometers in accordance with AIS-175 guidelines.
Until now, India’s emission standards relied on the Modified Indian Driving Cycle (MIDC), a laboratory-based method that often produced results differing from real-world conditions. WLTP, already in use across Europe, is designed to better reflect actual driving patterns, offering a more accurate assessment of CO₂, NO₂, and particulate emissions.
From April 2027, all new vehicles sold in India must meet WLTP-compliant standards. The update coincides with the introduction of Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) 3 regulations, which will further tighten fuel efficiency and emission requirements.
For electric vehicles, the WLTP test will provide more accurate real-world range estimates, replacing the laboratory-only figures used previously.
Currently, the WLTP adoption focuses on pollutant measurement under BS6 norms, but it is expected to expand to include fuel efficiency under CAFE regulations, providing a unified, globally-aligned testing framework for vehicles in India.

Tata Unveils First Image of 2026 Punch EV Facelift Ahead of Launch